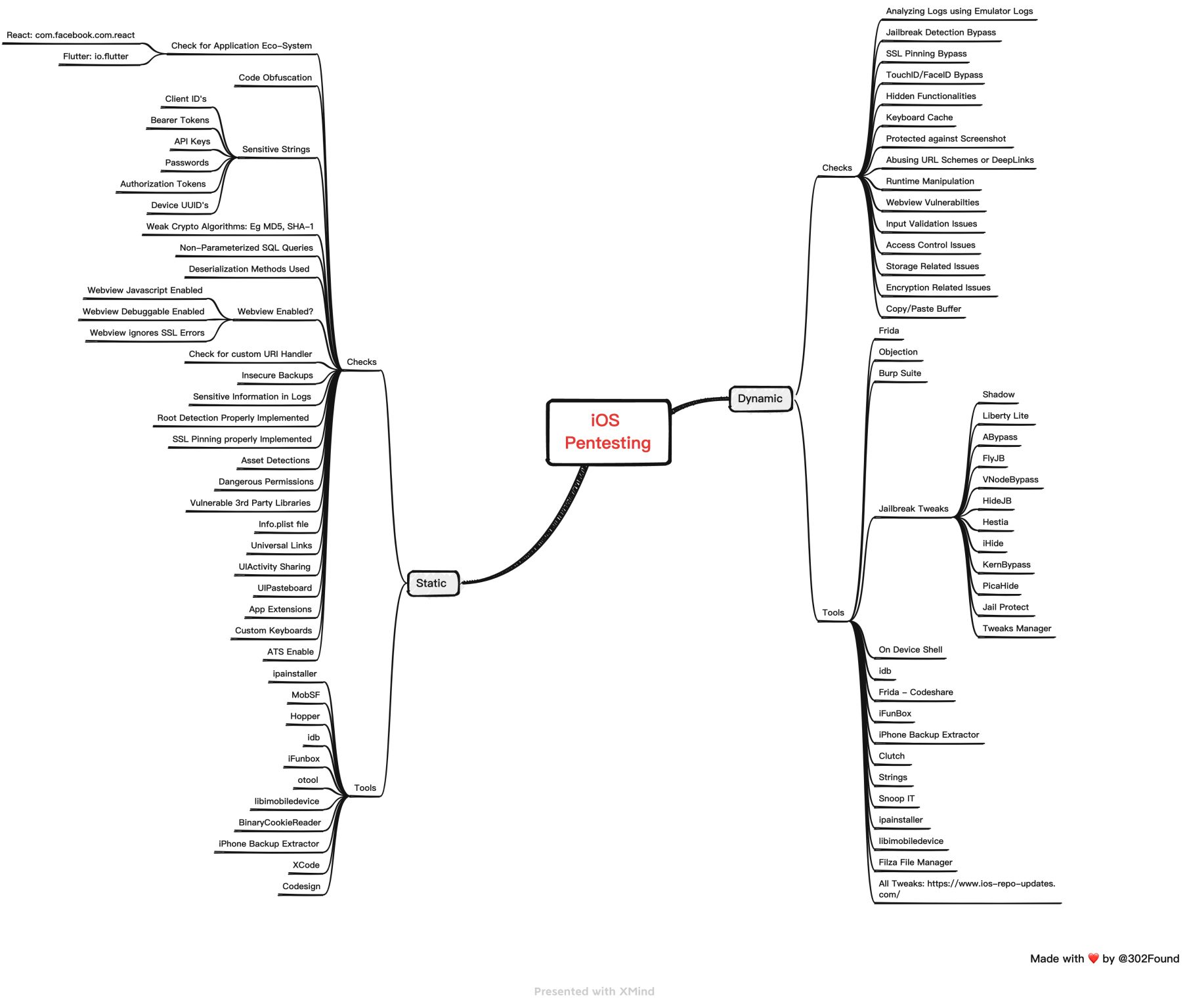
Iphone Security
- Static and Dynamic Analysis
-
Setting up the Mac Environemt environment below are the links IOS Download
-
I thought initially
IOSfor all of the apple family, but their different names their devices.
| Device | OS |
|---|---|
| Iphone | iOS |
| Ipad | IpadOS |
| iWatch | WatchOS |
| Macbook | macOS |
IOS Operating System
- IOS is a mobile operating system that Apple Inc. has designed for its iPhones, Second most popular and widely used after android.
The structure of the iOS operating system is Layered based. Its communication doesn't occur directly. The layers between the Application Layer and the Hardware layer will help with Communication. The lower level gives basic services on which all applications rely and the higher-level layers provide graphics and interface-related services. Most of the system interfaces comes with a special package called a framework.
-
A framework is a directory containing dynamic shared libraries, such as .files, header files, images, and helper applications that support the library. Every layer has its associated frameworks useful for a developer.

-
CORE OS
- It supports 64 bit enables the application to run faster
- All the IOS thechnologies are built under the lowest level layer i.e. Core OS layer. These technologies include:
- Core Bluetooth Framework
- External Accessories Framework
- Accelerate Framework
- Security Service Framework
- Local Authorization Framework etc
- CORE SERVICES
- Some important frameworks are present in the Core Services layer which helps the iOS os to cure itself and provide better functionality. It is the 2nd lowest layer in the Architecture, below frameworks are present in this layer.
- Address Book Framework: The Address Book Framework provides access to the contact details of the user.
- Cloud Kit Framework: This framework provides a medium to transfer data between your app and iCloud.
- Core Data Framework: It is the technology used to handle the data model of a Model View Controller app.
- Core Foundation Framework: This framework offers data management and service features for iOS applications.
- Core Location Framework: This framework helps in delivering location and heading information to the application.
- Core Motion Framework: All the motion-based data on the device is accessed with the help of the Core Motion Framework.
- Foundation Framework: Objective C covering too many of the features found in the Core Foundation framework.
- HealthKit Framework: This framework handles the health-related information of the user.
- HomeKit Framework: This framework is used for talking with and controlling connected devices with the users home.
- Social Framework: It is simply an interface that will access users' social media accounts.
- StoreKit Framework: It provides support for purchasing content and services from within iOS apps.
- MEDIA LAYER
- This layer helps, Enable all graphics video, and audio technology of the system. This is the second layer in te architecture. The different framework of MEDIA layer are:
- ULKit Graphics: This framework provides support for designing images and animating the view content.
- Core Graphics Framework: This framework support 2D vector and image-based rendering and it is a native drawing engine for iOS.
- Core Animation: This framework provides the optimum animation experience of the apps in iOS.
- Media Player Framework: This framework supports the playing of the playlist. It enables the user to use their iTunes library.
- AV Kit: This framework offers a number of easy-to-use interfaces for video presentation and recording, and even playback of audio and video.
- Open AL: This framework is also an Industry Standard Technology for Audio provision.
- Core Images: This framework offers advanced support for motionless images.
- GL Kit: This framework manages advanced 2D and 3D rendering by hardware-accelerated interfaces.
- COCOA TOUCH (APPLICATION LAYER)
- COCOA Touch is also known as the application layer which acts as an interface for the user to work with the iOS Operating system. It supports touch and motion events and many more features. The COCOA TOUCH layer provides the following frameworks :
- EvenKit Framework: This framework shows a standard system interface using view controllers for viewing and changing events.
- GameKit Framework: This framework even allows users to share game related data online via a Game Center.
- MapKit Framework: This framework provides a scrollable map that may be inserted into the user interface of the app.
- PushKit Framework: This framework provides for registration.
iOS Applications
- iOS Applications are zipped packages under the extension
.ipaA completed application ready to install is called a bundle. - Decompressing an IPA will have Name.app which contains following files:
- Info.plist: Specific Application Components
- _CodeSignature/: Plist file with signature over all files in the bundle.
- Assets.car: Zipped file containing assets.
- Frameworks/: Folder containing framework files
- Core Data: Used to save your application's permanent data for offline use, to cache temporary data, and to add undo functionality to your app on a single device.
- Pkginfo: Alternative way to specify the type and creator code of your application or bundle.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Info.plist is a xml file, Consists of Structured key-value pairs |
App Permissions:UageDescription, Custom URL schemas:CFBundleURLTypes, Exported/Imported custom document types:UTExportedTypeDeclarations, UTImportedTypeDeclarations, App Transport Security:NSAppTransportSecurity |
| UDID Unique device identifier | 40 digit unique sequence of letters and numbers to identify any iOS device, UDID found on the finder app on the macOS, UDID important gives the details of iOS device details. |
| On-device Shell | you can get a shell terminal on your iphone using some tweaks such as Mterminal, this can perform all the commands as the computer |
| Transferring data between device to PC | Command scp -P 22 root@<ip_address>:<path_of_file> <destination_path> |
Extracting IPA file
- Most of the times you don't get the source code of the from the developer, Since extraction is important.
- They encrypted with strong encryption key, Se we have the 3 types
- frida-ios-dump Code
- Install frida on device, Install prerequsits
sudo pip install -r requirements.txt --upgrade, keep this seperate teriminal in commandiproxy 2222 22(any port), Commandrun ./dump.py <App_Name> or <Bundle Identifier>
- Install frida on device, Install prerequsits
- Filza (Download from the Third-party AppStore
Sileo)- Go to Filza then
/var/container/Bundle/Application/<App_Name>, Create copy of the app you want, copy this inside the payload(You need to create) folder, then paste the inside the payload folder, then make zip of the file and then chnage it to the.ipa, then transfer scp -P 22 root@ :
- Go to Filza then
- iMazing
- Toolket perform actions using
https://imazing.com/download, You can only run on the same device of UDID, Not another IOS device.
- Toolket perform actions using
- Sideloading Install apps using 3U tools
- Sideloading is a method of installing applications by manually signing them.
- There are various applications which do this, but most common one used is AltStore.
- AltStore signs the IPA file and sideloads it.
iOS Basics for Mitigations
- Basics for Mitigations
Data Protection in iOS
- How the
File Contentsis encrypted in the iOS device
- Complete Protection
NSFileProtectionComplete- it's derived from the user passcode of the device UID protects the class key, Once the device is locked class key will wiped off from the memory, It will inaccessible until the user unlocks the device. - Protected Unless Open
NSFileProtectionCompleteUnlessOpen- It's same like but the class key is never expires after devoce locks, still the file contents accessable for the apps running in the background. - Protected Until First User Authentication
NSFileProtectionCompleteUntilFirstUserAuthentication- This file can be accessed as soon as the user unlocks the device for the first time after booting. It can be accessed even if the user subsequently locks the device and class key is not removed from the memory. - No Protection
NSFileProtectionNone- The key for this protcetion class is protected with the UID only. The class key is stored in "Effaceable Storage", which is a region of flash memory on the iOS device that allows the storage of small amounts of data. This protection class exists for fast remote wiping (Immediate deletion of the class key, which makes the data inaccessible).
Keychain
- Is a encrypted container, It will be accessiable autorized apps or same app can retrive the contents.
- The iOS it own password for the keychains stores encypted format.
- The password encrypted with AES created by PBKDF2 with Salt(device UID) to decrypt file contents.
kSecAccessControlPasscode: Access the item via a passcode.kSecAccessControlDeviceBiometryAny:Access the item via one of the fingerprints registed to Touch ID. Adding or removing a fingerprint won't invalidate the item.kSecAccessControlBiometryCurrentSet: Access the item via one of the fingerprints registered to Touch ID. Adding or removing a fingerprint will invalidate them item.kSecAccessControlUserPresence:: Access the item via either one of the registered foingerprints (using Touch ID) or default to the passcode.
Application Capabilities & Purpose Strings
- Each app has a unique home directory and is sandboxed, so that they cannot access protected system resources or files stored by the system or by other apps.
- Purpose Strings or usage description strings are custom texts that are offered ti users in the system's permission request alert when requesting permission to access protected data or resources.
- These can be found inside the
Info.plistfile
iOS App Extenions
-
Assume
Host Appis your notes, want to share with your friendApp Extensionis your sharing app lime Messages so notes copy the contents in the notes to send whomever your like.
-
App extenions let apps offer custom functionality and content to users while they're interacting with other apps or the system. Some of them are:
- Custome Keyboards: Replace the iOS system keyboard with a custom keyboard for use in all apps.
- Share: Post to a sharing website or share content with others.
- Today: Also called widgets, thay offer content or perform quick tasks in the Today view of Notification Center.
iOS Device Management
- From iOS verion 6, there is
built-in support for device managementcapabilities with fine grain controls that allows an organization to control the corporate appl;e devices. - The user can see the installed policies in settings -> General -> Profile and Device Management
- The profile are tied to the deviceID, signed and encrypted by the MDM server and temper proof. They cannot be removed without losing all the corporate data.
Mobile 2016 OWASP Top 10
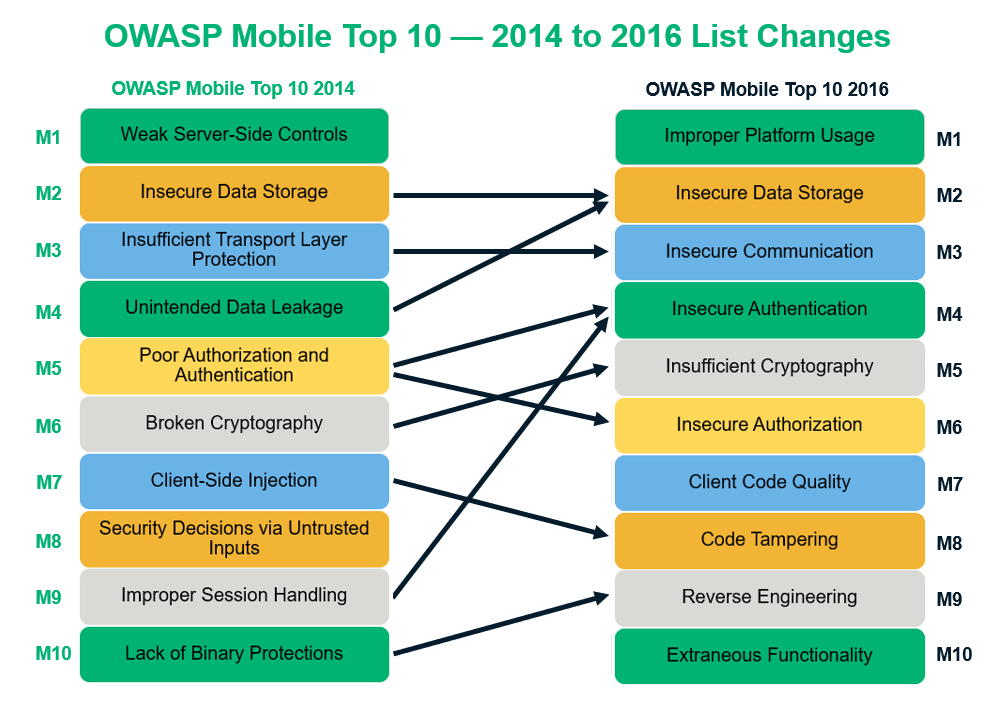
M1: Improper Platform Usage
- Misuse of a platform feature or failure to use platform security controls
- Examples include
- Platform Permissions
- Misuse of TouchID
- Misuse of Keychain
- Violation of guidelines
M2: Insecure Data Storage
- Insecure data storage vulnerabilities occur when development teams assume that users or malware will not have access to a mobile device's filesystem and subsequent sensitive information in data-stores on the device Example include
- Sensitive data stored in SQLite
- Sensitive data stored in Log Files
- Improper authentication of Firebase
M3: Insecure Communication
- Mobile applications frequently do not protect network traffic. They may use SSL/TLS during authentication but not elsewhere. This inconsistency leads to the risk of exposing data and session IDs to interception. The use of transport security does not mean the app has implemented it correctly.
- Usage of older SSL/TLS Libraries
- SSL Pinning Bypass
- Privacy Information Leakage
M4: Insecure Authenication
- Poor or missing authentication schemes allow an adversary to anonymously execute functionality within the mobile app or backend server used by the mobile app.
- Weak password policy
- Leaking OTP in response
- Leakage of sessions IDs
M5: Insufficient Cryptography
- An adversary can return encrypted code or sensitive data to its original unencrypted form due to weak encryption algorithms or flaws within the encryption process.
- Using no Encryption techniques
- Using weak hashing algorithms like MD5
- Using weak encryption algorithms like SHA-1
OWASP Remaining M6, M7, M8, M9, M10
- M6: Insecure Autorization: Autorization is the act of checking that the identified individual has the permissions necessary to perform the act. Authorisation checks should always immediately follow authentication of then an incoming request from a mobile device.
- Hidden Endpoints
- IDORs
- M7: Client Code Quality: Code quality issues are found frequently within most mobile code. The primary goal is to execute foreign code within the mobile code's address space.
- Memory Leaks
- Buffer Overflow
- M8: Code Tempering: An adversary modify code via malicious forms of the apps hosted in third-party app stores. The attacker may also trick the user into installing the app via phishing attacks. Mitigation is
Signature check from the developer- Changing the certificate to bypass SSL Pinning.
- Changing the API version.
- M9: Reverse Engineering: All mobile code is susceptible to reverse engineering. Code written in languages/frameworks that allow for dynamic introspection at runtime (Java, .NET, Objective C, Swift) are particularly at risk for reverse engineering.
- Reveal information about backend server
- Recon servers
- M10: Extraneous Functionality: Functionality that exposes information related to back-end test, demo, staging, or UAT environemts should not be included in a production build.
- Downloading configuration files.
- Examining log files.
Static Analysis iOS
- Find in the source code of the application certain hard-coded key, Insecure permissions and authentication, Insecure encryption and hashing without running the application
- Static analysis is about decompiling the IPA file and checking out for code related vulnerabilities.
- Checking out for file permissions
- Checking out for file permissions
- Checking out for insecure API, Functions
MobSF iOS
- Mobile Security Framework(MobSF), Its an automated all-in-one mobile application penetesting framework, Helps to perform runtime assessment.
- Reports can be downloaded in PDF format and Open-source MobSF tool.
- Info.plist security issue permission camera, Lack TLS
- Binary insecure APIs
_fopen, _strncpy, _memcpy, _strcpy, _printf, _strlen - Binary functions
_random,_mallocleads to memory leakage instead of calloc - Binary Logging functions
_NSLogfunction for logging - WebView based on the sensitive information
- Frida, Objection tools for the File system analysis
App Log Analysis
- To check for application logs for sensitive data following needs to be performed:
- Goto Xcode -> Devices and Simulators -> View device logs to see the logs.
- Grep the logs for sensitive data files
- If Linux
idevicesyslog | grep <your_app>
Hardcoded Credentials: MobSF
- Many developers hard coded credentials in the app, search for secret, crypt, private, token etc.
- Many apps use third party backend systems, analyse and .json and .xml files for credentials.
- Many apps contain hidden features, search for develop, debug, fake, test in the app binary.
- Check for different .plist files such as
GoogleService-Info.plist. These might contain juicy API keys.
SQLite Database: Core Data
- Core Data is a framework for managing the model layer of objects in your application.
- Core Data can use SQLite as its persistent store.
- SQLite Core Data information of an application in the path oen using filza application to this path
/private/var/mobile/Containers/Data/Application/{APPID}/Library/Applicationsupport. - Note: If SQLite Database can be opened and sensitive information can be accessed then a misconfiguration can be found.
Other SQLite Databases
- There is a chance that other SQLite Databases can also be found in an iOS application such as YapDatabases, Couchbase.
- These may be storing sensitive data on them and leaving it unencrypted.
- The can be found inside the application folder:
/private/var/mobile/Containers/Data/Application/{APPID}
- You can use the below command to find the databases of the application:
find ./ -name "*.sqlite" -or -name "*.db"
Firebase Misconfiguration (.json)
- Firebase is a NoSQL Cloud-based database.
- The database is stored in JSON format and synchronised in real time.
- If find a firebase string, there might be a chance that it might be misconfigured. Navigate to the URL kind of this
https://<path_of_the_file>/.json, Comes under Insecure Data Storage - If the response is:
- Permission Denied: This means that you cannot access it, so it's well configured
- Null response or a bunch of JSON data: This means that the database is public and you at least have read access.
iOS Keychain
- iOS Keychain is one of the best ways to store ypur secrets.
- But sometimes developers do not store them properly and hence this leads to leakage of such secrets.
- commaand to find secrets from keychains
ios keychain dump>frida-ps -Ua # It gives list of apps open, then open the DVIAswiftv2, see "com.highaltitudehacks.DVIAswiftv2.TF2TX3U8WG" > objection --gadget com.highaltitudehacks.DVIAswiftv2.TF2TX3U8WG explore # Open the application enter data submit > objection --gadget com.highaltitudehacks.DVIAswiftv2.TF2TX3U8WG explore # you see the data entered in the application
iOS UIPasteboard
- UIPasteboard enables sharing data within applications. 2 types
ios pasteboard monitor- Systemwide Pasteboard: Sharing data with any application.
- Custom Pasteboard: Sharing data with app having same team ID.
- An application can also prevent its users to copy sensitive data to the clipboard which is recommended
- Custom pasteboards can be creatd using pasteboardwithName:create or pasteboardWithUnique. The should not be used to these are deprecated since iOS 10. For Dynamic analysis, Objection pasteboard monitor can be used.
iOS WebViews
- These 3 types in iOS
- UIWebView: It is deprecated starting on iOS 12 and should not be used. Javascript can be disabled
- WKWebView:
- JS is enabled by default but disabled by javascriptEnabled properly
- JavaScriptCanOpenWindowsAutomatically properly can be used to block opening of new windows.
- hasOnlySecureContent properly can be used to verify resources are received using encrypted communication.
- SFSafariViewController:
- JavaScript cannot be disabled.
- Shares cookies and website data with Safari.
- Th user's activity and interaction are not visible to the app.
iOS Hot Patching/Enforced Updating
- Developers can remotely patch all installations of their app instantly without having to resubmit the application to the App store and wait until it's approved.
- Applications should be forced updated.
- Try downloading an older version of the application and check if it allows forced update or not.
Sensitive information inside Application Memory
- Somewhere or the other sensitive data is definitely going to be stored in memory.
- We first dump the memory of the application suing objection or frida then
strings memory > strings.txt - The file can be then opened using any text editor.
Insecure APIs/Functions
| Insecure Functions | Command |
|---|---|
| Weak Hashing Algorithms (MD5 & SHA1) | otool -Iv <app> | grep "MD5" |
| Random Functions (random, srand, rand) | otool -Iv <app> | grep "random" or "rand" |
| Insecure Memory Allocation (malloc) | otool -Iv <app> | grep "malloc" |
| Vulnerable Functions (gets, memory, strncpy,strlen,vsnprintf,sscanf,strtok,alloca,sprintf,printf,vsprintf) | otool -Iv <app> | grep "gets" |
Dynamic Analysis iOS
- Here we are sending request and response trying to change the request observe response, trying to break the functionality.
- Tweaks are often used to bring extra features or customisation options to your device. (Tweaks installed only Jailbroken device)
- These are applications that can be installed using root privileges of the iOS device.
- In iOS pentesting, tweaks are going to help us bypass a lot of issues which we would be looking in coming sections.
- Substitute is a default application that gets installed when the device gets jailbroke.
- The app allows you to fine tune substitute and control tweak injection
- Attempts to prevent processes with memory limits from crashing.
- Cydia & Sileo
- if Jailbroken your device using palerin Sileo, using Uncover, checkrin you get the Cydia, both GUI interface of APT for iOS
- It enables a user to find and install software not authorized by Apple on jailbroken.
- Third-Party App Store from where tweaks can be installed
Installing Frida
- Add the repo link in the
Sileo or cydiaadd the source install the app. Search repo here - Add the
https://build.frida.re/, then install the Frida app. To confirm installed or not usingfrida-ps -Ua
Jailbreak Detection bypass
- Firda So to allow tweaks you require Jailbreak.
- Jailbreak Detection mechanism which is implemented by the developers, app cannot work on jailbroken device.
- However some developers do not consider this as a best practice, While those who implement it, might not implement properly. below js file
- Jailbreak detection bypass using
frida -U -f package_id -l jailbreak.js - Shadow add the source
https://ios.jjolano.me/then install theshadowapp, click onAlways-Onby default for all the apps or select specific you bypass the detection. - Liberty add the source
https://ryleylangus.com/repo/then install Liberty Lite, Enable Liberty check the DVIA application check the jailbreak detection it's upto iOS 14 not sure after the verions - A-Bypass add the source
http://repo.co.krthen install, it support modern apps, - Other Jailbreak Detection LINKS - FlyJB, HideJB, Liberty Lite, VNodeBypass, Hestia, iHide, KernBypass
Objection
- Objection is a runtime mobile exploration toolkit, To install objection simply run command
pip3 install objection, frida, frida-tools - Explore the package using
objection --gadget package_name explore - Disable jailbreak detection using
ios jailbreak disable
SSL Pinning and Bypass using Frida
- SSL Pinning is a technique that most application owners implement so that any request sent by the mobile application is not intercepted.
- SSL pinning is considered as the first and the most important step in the security mechanism of an application. But due to improper means, SSL Pinning can usually be bypassed.
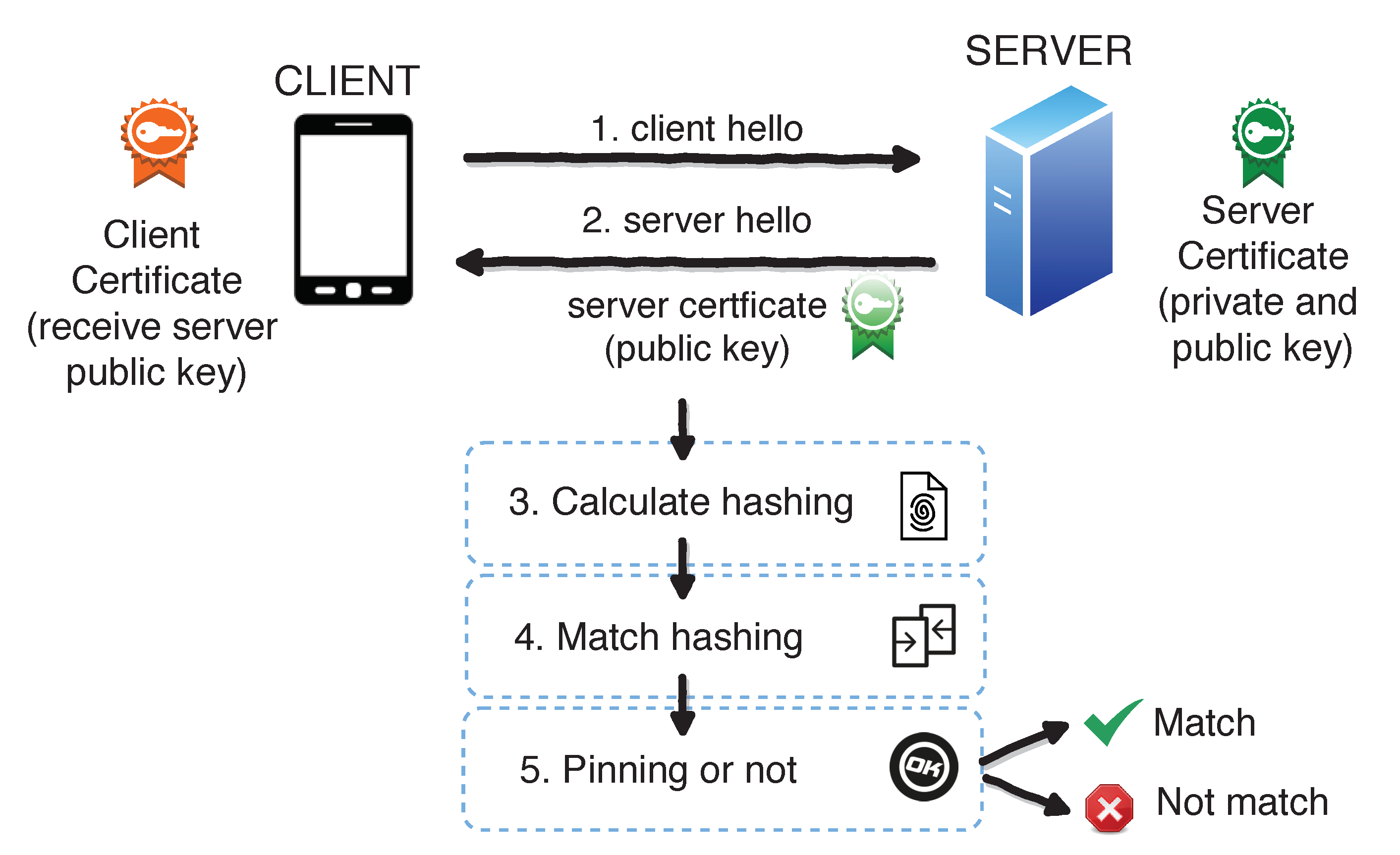
- Check the package name using the
frida-ps -Usthen scripty is sslpinning.js run this commandfrida -U -f package_id -l sslpinning.js - SSL Kill Switch2 Enable SSL byass, it will bypass all the SSL restrictions.
- Objection the package using
objection --gadget package_name explorethen Disable SSL Pinning detection usingios-sslpinning-disable
Local Authentication Mechanism Bypass
- Objection the package using
objection --gadget package_name explorethen Disable Authentication detection usingios ui biometrics_bypass - Non jailbroken device
objection exploreopen the app DVIAswiftv2 app then Touch/Face ID Bypass menu, then hook with objection terminalios ui biometrics_bypass - Try to cover the face then it will ask for the password, the tool objection going to bypass the password restriction [Udemy IOS pentesting Vaibhav Lakhani]
Demo
- Download the App in Non-Jailbroken iphone
- Created .ipa file using this process
- Static Analysis
- MobSF for automated analysis
- Dynamic Analysis
- Setup a Burpsuite with Base OS IP address, In the phone set manual proxy with your IP
- Enable the SSL Kill Switch2 in an app enforces any ssl this bypass the that.
- Try to capture webapp issues
Frida without Jailbreaking
- Find the valid security Identity for codesigning the IPA file:
security find-indentity -p codesigning -v
- Patch and inject Frida server in the IPA using objection
objection patchipa --source Application.ipa --codesign-signature
- Unzip the newly created IPA using the commands
unzip Application-frida-signed.ipa
- Install the patched IPA to the iOS Device
ios-deploy --bundle Payload/SomeAppName.app -W -d
- Keep the terminal command running and run objection on a new terminal
- objection explore